Test Code:
3462
Clinical Use
- Diagnose bladder cancer in patients with hematuria (in conjunction with standard diagnostic procedures)
- Detect bladder cancer recurrence
Clinical Background
Bladder cancer is the fourth most common cancer in men and the ninth in women, with a combined estimate of 63,210 new cases in the U.S. in 2005.1 Non-invasive, superficial cancers can usually be cured, especially when well differentiated. Many bladder cancers, however, will recur: despite complete tumor resection, about 66% of patients will have a recurrence within 5 years and 88% within 15 years. Frequent monitoring (up to four times per year) for early detection of recurrence is key to increased survival of these patients. Traditionally, cystoscopy-guided biopsy, followed by histology, has been used for initial diagnosis, and cystoscopy and voided urine cytology (VUC) have been used for monitoring.
Vysis UroVysion is a molecular cytology test that detects aneuploidy of chromosomes 3, 7, and 17 and deletion of the 9p21 locus via fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) in urine specimens. In a study of 497 patients with hematuria, the Vysis UroVysion test showed a diagnostic sensitivity of 69% and specificity of 78% compared with cystoscopy followed by histology. The positive and negative predictive values were 27% and 95%, respectively (prevalence, 10.8%).2 Thus, the Vysis UroVysion test appears useful for diagnosis of bladder cancer in patients with hematuria.
Researchers have found that increased chromosomal instability and aneuploidy, such as that detected by the Vysis UroVysion test, are characteristic of bladder tumor progression. Due to its high specificity (~96%) and increased sensitivity (Figure 1),3 the Vysis UroVysion test is useful for early detection of bladder cancer recurrence when used in conjunction with cystoscopy. When the Vysis UroVysion test is positive and cystoscopy is negative, cancer recurs on average 4 months earlier than when both tests are negative; thus, a positive Vysis UroVysion test may indicate a need for increased surveillance in these cases.
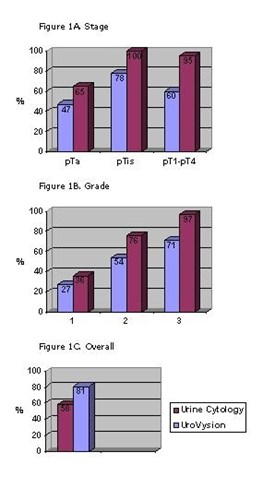
Figure 1. Sensitivity of the Vysis UroVysion test as compared to that of urine cytology. Figure 1A shows sensitivity for tumor stages PTa, PTis, and PT1-PT4; Figure 1B shows sensitivity for tumor grades 1, 2, and 3; and Figure 1C shows overall sensitivity.3
Method
In this fluorescence in-situ hybridization (FISH) method, a mixture of CEP 3, CEP 7, CEP 17, and LSI p16 probes, each labeled with a different fluorchrome, is used to enumerate chromosomes 3, 7, and 17 and detect the 9p21 locus deletion on chromosome 9.
Interpretive Information
A positive result is consistent with a diagnosis of bladder cancer or bladder cancer recurrence, either in the bladder or in another site within the urinary system. A negative result is suggestive of the absence of bladder cancer but does not rule it out.
Specimen Requirements
UroCyte Collection Kit available through our warehouse (supply #19343). Follow the instructions included with the kit.
CPT Codes*
88368 x4
Pursuant to a directive from Noridian, all Medicare claims must reflect CPT 88299. This CPT is subject to Noridian’s local coverage determination for Cytogenetic Studies. An ABN should be collected from Medicare Beneficiaries if their diagnosis does not meet Noridian’s coverage guidelines. All other billing will continue under the original published CPT coding.
References
1. Leading sites of new cancer cases and deaths. American Cancer Society Web site. Available at: http://www.cancer.org/downloads/stt/Leading_Sites_of_New_Cancer_Cases_and_Deaths_2005_Estimates.pdf. Accessed September 15, 2005.
2. UroVysionTM Bladder Cancer Kit – P030052. Food and Drug Administration Web Site. Available at: http://www.fda.gov/cdrh/pdf3/p030052b.pdf. Accessed September 15, 2005.
3. Halling KC, King W, Sokolova IA, et al. A comparison of cytology and fluorescence in situ hybridization for the detection of urothelial carcinoma. J Urol. 2000;164:1768-1775.
* The CPT Codes provided are based on AMA guidelines and are for informational purposes only. CPT coding is the sole responsibility of the billing party. Please direct any questions regarding coding to the Payor being billed.
All third-party marks - ®’ and TM’ – are the property of their respective owners.
